Most cats must be sedated or anesthetized to perform a thorough examination. Nasopharyngeal polyps are not common but they can cause significant distress to affected cats.
Animal Surgical Center Of Michigan Veterinarian In Flint Mi
Simply pulling out the polyp will quite frequently be sufficient to remedy the problem.

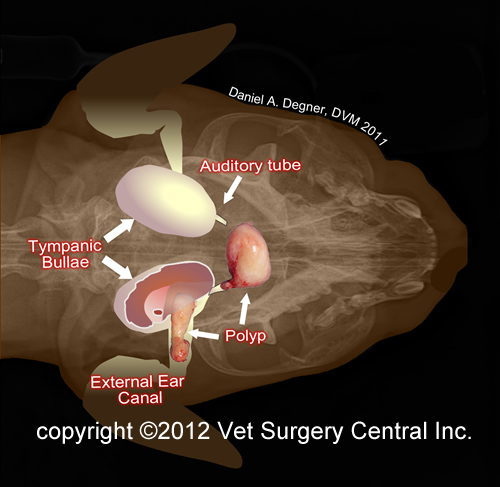
. Nasopharyngeal polyps are benign growths that arise from the mucous membranes of the nose nasal or the base of the eustachian tube nasopharyngeal. What is the prognosis for cats with polyps. The polyp at the back of the pharynx may be plucked out but there can be a tendency for it to grow back particularly if it has extensions into the middle ear or the ear canal.
The cat is anesthetized he says and the veterinarian will grab the polyp with a tiny forceps and yank it out. The two most common approaches are polyp removal by traction prednisolone therapy and ventral bulla osteotomy. In most cases.
Since nasal polyps are growths causing partial obstruction along the cats nasal passages andor ear canals the ideal treatment is the surgical removal of the benign mass. Some cats may have nasal discharge can be clear or thick yellow snotty looking. Its stalk will usually come out along with it.
There is often a rapid improvement in the signs it showed before the surgery. Polyps can extend into the middle ear external ear pharynx cavity behind the mouth and nasal cavity. She said it could be a congenital abnormality or a mechanical obstruction whatever that is.
Feline nasopharyngeal polyps Vet Clin North Am Small Anim. De-bulking of the mass will generally improve the breathing and other clinical signs. A polyp grows from a small stalk but can become quite a substantial size.
The polyp should be removed along with its stalk which tapers at one end. Following removal of the polyps your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection of the surgical site. I found her as a stray a year ago and the vet told me she had chronic URI and we went through a couple rounds of antibiotics and steroids.
Nasopharyngeal polyps often cause upper respiratory tract difficulty. The cats small oral cavity prevented polyp removal via traditional nasopharyngoscopy and the owner declined rhinotomy because of concerns about postoperative morbidity. In this film Alasdair Hotston Moore MA VetMB CertSAC CertVR CertSAS FRCVS demonstrates how to remove a nasopharyngeal polyp in a cat.
Nasopharygeal polyps often present as a persistent snoring sound in cats. Its normally a very short procedure and the cat recovers quickly. Surgery to remove as much of the polyp as possible is the most common treatment.
Stone points out that they are almost always observed in young adults and occasionally kittens. Some cats will require a more serious surgery known as a Ventral bulla osteotomy. Surgical excision of an aural or nasopharyngeal polyp.
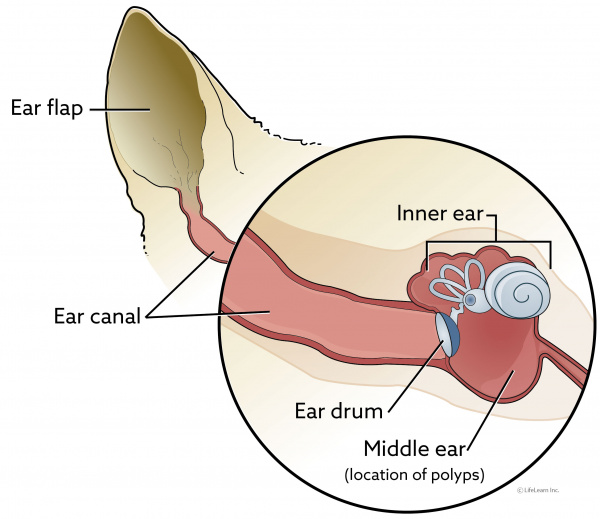
In cats with nasopharyngeal polyps growing out through the ear canal the polyps may be visible on deep inspection of the ear canal and eardrum. There are multiple options for removal of nasopharyngeal polyps. With your cat under general anesthesia your veterinarian will use forceps to grip twist and pull the polyp free from its attachment.
Polyps typically occur in younger cats. Ultimately the vet said she might have a growth but treatment would be like 10k and she was in no painwas fine. She suggested a CT scan for and to see a specialist to come up with a plan which involves lotsa.
Nasal polyps can often be surgically removed with traction or avulsion pulling or tearing. A novel endoscopic approach for the removal of nasal polyps from a cat with upper respiratory obstruction is described. Traction may be considered initially however the owner must be made aware of the likelihood of recurrence.
Unknown etiology however it is speculated that the polyps could be congenital or a response to an inflammatory. Aural-nasopharyngeal polyps are the most common nasopharyngeal disease of young cats and the most common non-neoplastic mass of the feline ear 12. Traction avulsion is the removal of a polyp from an anesthetized cat by gently and steadily pulling on the growth with a small.
Treatment he says is always surgical. Removal of as much of the polyp as possible will generally improve the breathing and other clinical signs. This is my cat Citra.
In summary an ideal diagnostic plan for cats with suspected FNPs should include a thorough anesthetized oropharyngeal examination otoscopic examination and imaging studies which may consist of a bulla radiographic series or specialized imaging studies such as CT or MR scans. The veterinarian applies steady traction on the polyp until it releases hopefully at its base. There have been some reports of success in treating the polyps by plucking and then giving the cat oral.
In most cases it is anatomically impossible to remove the entire polyp and recurrence is common. Local removal avulsion of a nasopharyngeal polyp will result in alleviation of clinical respiratory signs however recurrence rates of 15-50 have been reported if a. Easy-to-reach nasopharyngeal and ear polyps can be removed using gentle steady traction on the mass of tissue with the cat under general anaesthetic.
The range is 3 months to 18 years 3-7. Polyps located at the back of the mouth or throat can be gently plucked out using a pair of long surgical forceps through what is called an avulsiontraction technique. The vet said the possibility of nasal polyps is possible but highly unlikely due to his age at only 5 months old.
Treatment for nasopharyngeal polyps include appropriate. While seen in older cats other ruleouts would include neoplasia granuloma etc. Post-op treatment with pain relievers antibiotics and corticosteroids is necessary.
To claim time spent w. In the best case scenario a nasopharyngeal polyp can essentially just be pulled off the tissue from which it is growing either via the mouth or through the ear. Access to the nasopharynx was achieved by introducing an endoscope via.
Signs such as sneezing and difficulty breathing are common. Polyps are usually benign fleshy masses that emerge from the nose nasopharynx middle ear or external ear canal. Although nasopharyngeal polyps can develop in cats of all ages and are occasionally diagnosed in elderly cats Dr.
Chronic otitis externa head shaking otorrhea waxy or purulent discharge. Nasopharyngeal polyps can grow into the back of the throat obstructing the breathing passageways. Treatment of Nasopharyngeal Polyps in Cats.
The exact cause isnt entirely understood but it is believed that they are the result of chronic inflammation or congenital. Nasal discharge stertorous breathing reverse sneezing sneezing can interfere with swallowing. Polyps are seen in young to middle-aged cats with the mean age at presentation variably reported as 18 months 3-5 or 60 years 67.
Nasopharyngeal Polyps In Cats Vca Animal Hospitals

Nasopharyngeal Polyp In A Cat Removal Cost And Veterinary Advice Youtube

Nasopharyngeal Polyps American College Of Veterinary Surgeons Acvs

0 Comments